In today's fast-paced world, achieving peak mental performance is becoming increasingly important. Whether you're a student cramming for exams, a professional looking to increase productivity, or an elderly person looking to maintain cognitive function, the quest for cognitive enhancement is universal.
Choline is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various biological functions in the body. Despite the importance of choline, many people still don't know what it is and how it can benefit their health.
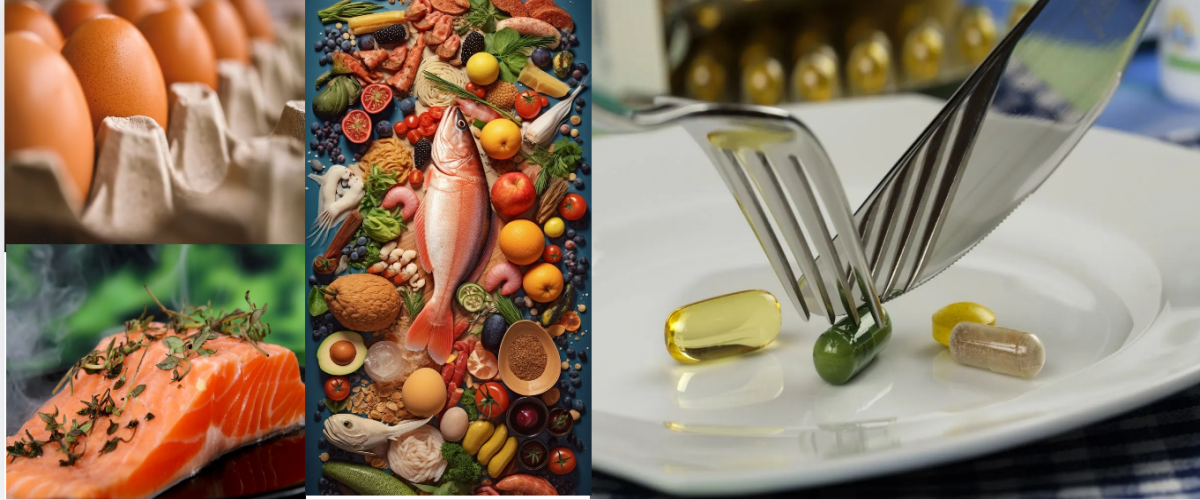
Choline is a water-soluble nutrient that belongs to the B vitamin family but does not qualify as a true vitamin. It occurs naturally in many foods such as eggs, liver, fish, soybeans and peanuts. In addition, it can also be synthesized in small amounts by the liver.
Choline's primary role in the body is as a precursor for the synthesis of the important neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine plays an important role in the function of the central nervous system, including memory, muscle control, and overall cognitive function.
In addition to its role in neurotransmitter synthesis, choline plays an important role in other physiological processes. It is an essential component of cell membranes and helps maintain their integrity and structure. Choline also contributes to the formation of phosphatidylcholine, a major component of lipoproteins that transport fat in the blood.
Although choline occurs naturally in a variety of foods, some people may have higher needs due to specific health conditions or genetic factors. For example, vegetarians and vegans may have difficulty meeting their choline needs because plant sources are often low in choline.
First, choline is a nutrient necessary for the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for a variety of brain functions, including memory, cognition, and muscle control. Without an adequate supply of choline, our brain's ability to efficiently transmit signals can be impaired, leading to impaired cognitive function and memory difficulties.
Many studies have linked choline intake to improved cognitive performance. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that pregnant women who consumed more choline during the third trimester had children with enhanced cognitive abilities, including better memory and concentration. Another study published in the Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society found that choline supplementation in adults improved verbal and visual memory.
In addition to its role in brain development and cognitive function, choline has been linked to a range of other health benefits. It helps maintain liver health by preventing fat buildup and promoting efficient processing of cholesterol and toxins in the liver. Choline also plays a role in regulating inflammation in the body, an underlying factor in various chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes and Alzheimer's disease.
Dietary sources of choline include eggs, liver, shrimp, and salmon. However, despite the importance of choline, surveys show that average choline intake is below recommended levels. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) state that the recommended daily intake of choline for most adults is 550 mg for men and 425 mg for women.
Although choline occurs naturally in a variety of food sources, some people may have difficulty meeting their daily requirements. In such cases, choline supplements can be a valuable addition to their diet. Supplements provide a convenient way to ensure optimal choline intake, especially for individuals with certain dietary restrictions or preferences.
◆Choline Bitartrate
Choline bitartrate, the basic form of choline, is a combination of the essential nutrient choline and a natural salt called bitartrate. From improving memory and concentration to supporting liver health and fetal development, choline bitartrate Alkali has many benefits.
◆Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholine is an important component of cell membranes and plays a vital role in various biological processes. It belongs to a class of phospholipids called phosphatidyls, which are the main building blocks of cell membranes.
Phosphatidylcholine consists of two fatty acids, a glycerol molecule, a phosphate group and a choline molecule. Choline is an essential nutrient for the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine in the body. It can be obtained through the diet or synthesized from methionine in the liver.
Phosphatidylcholines perform multiple roles in the body. It offers a variety of potential benefits, from maintaining cell membrane integrity to supporting brain health, liver function, and cardiovascular health. While it can be obtained through diet, supplements are popular for their targeted use.
◆Choline dihydrogen citrate
Dihydrocholine Citrate, also known as Choline Citrate or Citicoline, is derived from the combination of Choline and Citrate, two essential nutrients found in the human body.
It is also a water-soluble compound that occurs naturally in foods such as eggs, liver, and peanuts. It is also available as a dietary supplement in capsule or powder form.
The combination of choline and citrate in Choline Citrate provides many health benefits. One of the main benefits is its positive impact on brain function and cognitive health.
Additionally, Dihydrocholine Citrate supports liver health. Choline is essential for the proper functioning of the liver due to its role in fat metabolism and transport of fat from the liver.
CDP-choline, also known as Citicoline, is a naturally occurring compound found in every cell in the body. It plays a vital role in the synthesis and maintenance of cell membranes, especially in the brain. This important compound is involved in many physiological processes, making it an important factor in brain health and function.
CDP-choline is classified as a nootropic substance - a substance known to enhance cognitive function, memory and learning. It is a valuable nutrient that has been extensively studied for its potential benefits for brain health, especially age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
◆Alpha GPC (Alpha-glycerophosphocholine)
Alpha GPC, short for Alpha-Glycerophosphocholine, is a natural choline compound found in our brains as well as in certain foods. It is a precursor to acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter involved in various cognitive functions, including memory, learning, and attention. By increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain, Alpha GPC is believed to positively affect cognitive performance.
One of the main reasons people turn to Alpha GPC is its potential to enhance memory and learning. Numerous studies have shown that supplementation with Alpha GPC may improve memory formation and retrieval. In a clinical trial published in the journal Clinical Therapeutics, researchers found that Alpha GPC significantly improved memory and cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Similar positive effects on memory have been observed in healthy individuals.
◆Lecithin
Lecithin is a natural substance that is essential in our bodies and in various industries. It is found in many foods and is also produced by the human body. It is a fatty substance that belongs to a group of compounds called phospholipids. Lecithin plays a vital role in cellular function, especially in cell membranes.
The cell membrane acts as the cell's protective barrier, controlling the flow of nutrients and waste into and out of the cell. Lecithin helps maintain the integrity of these membranes by providing structural support and ensuring their fluidity. It also facilitates efficient communication between cells, allowing them to send and receive signals efficiently.
One of the main sources of lecithin in our diets is animal and plant foods. Internal organs such as egg yolks and liver are rich in lecithin. Other sources include soybeans, sunflower seeds, wheat germ, peanuts, and some vegetables. Additionally, lecithin is available as a dietary supplement in granule or capsule form.
Choline's role in the body:
Choline is an important nutrient that aids in the synthesis of phospholipids, which are critical for cell structure and function. It also aids in the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for supporting healthy brain function, memory, and muscle control. Additionally, choline helps reduce inflammation, prevent liver damage and support a healthy metabolism.
Choline in food:
A balanced diet can provide choline from a variety of food sources. Eggs, liver, salmon, beef, broccoli, peanuts and soybeans are rich natural sources of choline. However, it is important to note that the amount of choline in foods may vary, and cooking methods may affect its availability. For example, hard-boiling eggs can reduce their choline content by up to 20%. Therefore, cooking techniques that preserve the choline content of foods must be considered.
In addition, choline is often contained in fortifiers of some grain products, such as bread and cereals. This fortification helps increase choline availability in those with limited natural sources or who follow specific dietary restrictions.
Choline Supplements:
Choline supplements have become increasingly popular due to their convenience and ease of ensuring adequate intake. Various forms of choline are available as supplements, including choline bitartrate, choline chloride, and citicoline. These supplements are designed to close the gap between dietary intake and the recommended daily intake of choline (550 mg for men and 425 mg for women).
Supplements are especially beneficial for individuals following certain dietary patterns, such as vegetarians or those who have difficulty obtaining choline-rich foods. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it meets your health goals and needs.
Foods and Supplements: Making the Best Choices
While supplements can provide a convenient way to meet your choline needs, it's important to prioritize a balanced and varied diet. Choline obtained from food sources is packed with other essential nutrients and compounds that work synergistically to support overall health.
Ideally, focus on incorporating choline-rich foods into your diet. Including eggs, liver, fish, and leafy greens, along with a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help ensure you get enough choline.
Choline is an essential nutrient known for its important role in cognitive function, memory formation and overall brain health. It is classified as a water-soluble vitamin-like compound that is naturally produced in the liver, but can also be obtained through dietary sources. It plays a vital role in the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for a variety of cognitive processes, including attention, learning and memory.
▲The Role of Choline in a Nootropic Stack
When it comes to enhancing cognitive function, many people turn to nootropic combinations -- combinations of different compounds designed to optimize brain performance. These stacks often contain choline due to their cholinergic properties. By providing the brain with an adequate supply of choline, nootropic users aim to maximize the production and release of acetylcholine, thereby enhancing their cognitive performance.
▲Choline and Nootropic Synergy
The presence of choline in nootropics has been shown to enhance the effects of other cognitive-enhancing compounds. For example, pairing choline with racemics (a class of nootropics) can provide a synergistic effect because racemics increase the brain's need for acetylcholine. By ensuring an adequate supply of acetylcholine with choline supplementation, these racemates can effectively exert their full cognitive benefits.
Aline has demonstrated its ability todditionally, cho counteract side effects commonly associated with certain nootropics, such as headaches or brain fog. By supplementing choline levels, users may experience smoother, more sustainable cognitive enhancement and eliminate unwanted side effects.
Q: What are some good food sources of choline?
A: Choline can be found in various food sources such as eggs, liver, fish, poultry, and certain nuts and vegetables. Including these foods in your diet can help meet your daily requirement of choline.
Q: Can I get enough choline from my diet alone?
A: It is possible to obtain sufficient choline through a balanced diet that includes choline-rich foods. However, some individuals may have increased requirements or limited access to choline-rich foods, making supplementation necessary.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any supplements or changing your healthcare regimen.
Post time: Aug-18-2023